What are Gate Valves?
Gate valves work exceptionally in many environments. There are many advantages of gate valves due to their efficient structure. People often mistake gate valves vs. Globe valves. The gate valve’s working is unique and differs from other valves. This comprehensive guide to gate valves covers everything you need to know about them. The working types and applications of gate valves are described below. Let’s check out what a gate valve is.
What is a Gate Valve?
A gate valve is a plumbing product that controls the fluid flow through pipes. Consider having a pipe that brings water, and you want to control when water flows and stops. In such conditions, gate valves are the most suitable option.
One of the best features of a gate valve is its excellent seal-on closure. This property ensures no liquid or gas leaks when the valve is closed. There are many types of gate valves for water supply and other applications.
Gate valves apply to house water pipes, big pipelines for transport, and power plants. The ideal usage of a gate valve is in regulating gas or liquid flow.
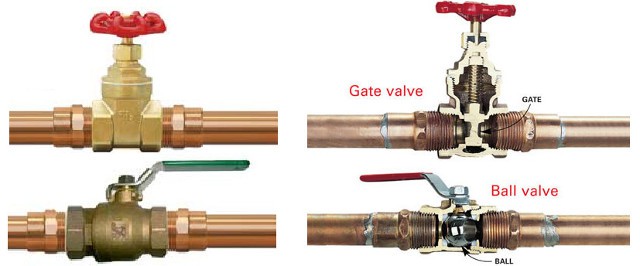
Symbol of Gate Valve:
The symbol of a gate valve contains a vertical line where two triangles meet. The triangles have extended solid lines on the opposite sides at the symbol terminal. In pipelines and instrumentation, the gate valve symbol is modified. As a result, the solid vertical line from the center of the triangles is removed.
Working of Gate Valves:
Gate valve working is like opening and closing a door to control the flow of water or air in a pipe. Consider having a giant door inside the pipeline. You can lift it to allow flow or lower it to stop it. The gate valve works similarly to this mechanism.

Open Position: The flow can pass through” when” the gate valve opens. The “door” inside the valve, called the gate, lifts, creating an open pathway for water or gas to move through the pipe.
Closed Position: When we want to stop the flow, we close the gate valve. The gate lowers, blocking the pathway inside the valve. Nothing can pass through when the gate is down, and the entire flow stops.
We use a handle to control the gate and move it up or down. Turning the handle lifts or lowers the gate, like opening or closing a door. It’s like a switch that we can use to control the flow in pipes. In our homes, in big pipelines for oil and gas, or in different industries, they manage the movement of fluids.
Gate Valve Specifications:
Here are the gate valve specifications.

| Product Name | Bronze Gate Valve |
| Material | Bronze |
| Size | 1/2,3/4,1“,1-14/”,1-1/2“,2”,2-1/2“,3“,4” |
| Thread | BSP, NPT |
| Temperature Range | -10°C to 120°C |
| Pressure | 200WOG |
| Operation | Handwheel |
Gate Valve Parts:
Gate valve parts vary for every type and condition of operation. Yet, some of the parts are mandatory for making up the structure. The body, gate, handle, bonnet, seat, etc., are essential gate valve parts. Let’s check out their description.
Gates:
The gate is the most crucial component that decides the gate valve’s performance. It comes in a variety of designs and variations to suit specific applications. Parallel and wedge-shaped gates are the most popular ones. Knife, slab, and similar expanding gates are other significant types. Each one of them differs due to its shape and working mechanism.
Gate Valve Body:
The gate valve body serves as a protective enclosure to hold all parts together. It is the point from where the fluid enters and leaves the valves after regulation. Depending on the material used, the valve bodies can be metallic, non-metallic, alloy, or plastic.
It is available in three variants for respective applications. These are cross-flow, reduced, or full-bore designs. The gate valve body also serves a connection purpose. The flanges, butts, wafers, or sockets join the valve with the system through the body.
Gate Valve Stem:
The gate valve stem is a central component that controls the disc movement. The rotation of the stem results in the direction of the disc, either lifting or dropping. This stem is directly connected to a handle or actuator to control the operation of the valve. It has a valve disc connection at one end and a handle connection at the other. This way, it maintains control of the functioning of the gate valve.
Gate Valve Bonnet:
Bonnets serve as a protective cover and support to gate valve parts. These parts include the stem, actuators, and disc. They also play a pivotal role in the operation of the branch. Gate valve bonnet material is often identical to that of the body. They connect with the bonnet with the help of bolts, threads, or welding. Some gate valves are bonnetless, as their bonnets are integrated into the body.
Gate Valve Seat:
The gate valve seat is crucial for the sealing mechanism and positioning of the disc. Usually, plumbing valves comprise one seat. But gate valves have two seats on the ends of each pipe flange. The correct position of the seat is highly significant for efficient sealing. If it remains unchecked, it can cause gate valve leakages.
Gate Valve Disc:
The gate valve disc is the part that allows the escape or blockage of fluid. It moves away from the seat to create a fluid pathway. Similarly, when it moves toward the center, it blocks the path. The mean position or resting point of the disc is the seat.
Yoke and Gland Packing:
Yokes are the arms of the gate valve. They form a connection between the handle and the stem. In some valve designs, they are merged into the bonnets.
Gland packings are secured in the stuffing box to prevent gate valve leakages. A unique structure called sleeves is used to keep it in the box.
Types of Gate Valves:
Here are the gate valve types.
Rising Stem Gate Valve:

The stem grows and lowers when turning the handle in rising stem gate valves. When we open the valve, the stem stretches and straightens. At the same time, the branch lies downwards when the valve is closed. This mechanism enables us to understand the valve status by looking at the valve design.
Non-Rising Stem Gate Valve:

The stem type in this gate valve remains stationary in its position. Instead, it remains still while the gate inside the valve changes its position from up to down. The best perk of having non-rising stems is their less space consumption. A non-rising stem gate valve is ideal for small spaces where giant valves cannot be installed due to a lack of space.
Wedge-Shaped Gate Valve:

The gate has a wedge shape in this type. It means the gate wedges between the valve seats when it lowers. They provide a very secure shut-off. They are excellent where a tight seal and resistance to high pressures are necessary.
Bypass Gate Valve:

Bypass gate valves have a unique structure containing an extra passage. This additional duct serves as a substitute when the gate valve is closed. The fluid can flow and continue its way through a closed valve via this bypass.
The primary purpose of a gate valve with a bypass is to maintain continuous flow. It continues to flow even during maintenance or repair activities on the gate valve itself. Opening the bypass allows fluid to move through the system. At the same time, the gate valve works without interrupting the flow.
Gate Valve Standards:
Here are gate valve standards you should consider before making a selection.
- API B16.34 for Pressure Temperature Rating.
- API 598 for Pressure Testing.
- API 600 for the design, material, and testing of steel gate valves.
- ANSI B16.10 for Face-to-Face.
- NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) for fire protection systems.
- AWWA (American Water Works Association) for wastewater and water applications.
Considering gate valve standards while buying is essential to ensure safety and reliable performance. There could be a few other standards that you could come across at the time of selection. You should consult a credible B2B gate valve manufacturer for custom solutions and plumbing assistance.
Gate Valve Applications:
Here are a few of the most helpful gate valve applications.

Water Supply Systems:
Gate valves regulate water flow through pipes in water supply systems. There are separate types of gate valves for water supply systems. They have immense switch-like structures that can be turned on or off at different locations, such as our homes and schools. When you turn the tap on to wash your hands, a gate valve helps control water flow through the pipes. It is one of the best applications for gate valves.
Gas Pipelines:
Gate valves are crucial in gas pipelines that carry natural gas to homes for cooking and heating. They help regulate gas flow, ensuring the correct amount reaches each place.
Power Plants:
In power plants, gate valves serve the duty of regulating steam and water flow. Steam generates electricity, and gate valves take steam to the desired locations with excellent carrying ability. Similarly, you can turn off the flow from the gate valve when unnecessary.
Irrigation Systems:
Gate valves play a role in irrigation systems present in farming. It is among the best gate valve applications. They control the flow of water within fields during agricultural operations. They equalize the water supply for the growth of healthy crops.
Oil and Gas Industries:
Gate valves help in controlling the flow of oil and gas. They enhance safety and bring them to their destination with great care.
Chemical Processing:
Gate valves in chemical plants control the chemical flow during the manufacturing process.
Water Treatment Plants:
Water treatment plants utilize gate valves to regulate water flow during the purification process. They ensure clean and safe water reaches our homes for drinking and other activities.
Sewage Systems:
Gate valves in sewage systems control wastewater flow and prevent any backflow.
Gate Valve Material Selection:
Gate valve material selection requires consideration of certain factors. It includes pressure and temperature, flow rate, and fluid type. Here are some of the most common gate valve materials and their features.
Stainless Steel: It is suitable for applications like chemicals, petrochemicals, oil, and gas. This material can handle corrosive fluids and can operate under high-pressure conditions.
Carbon Steel: It efficiently deals with fluids with moderate pressure, temperature, and non-corrosive media. The applications include steam, gas, and water.
Bronze: It is best for moderate flow rates in seawater and brine. Bronze is resistant to saltwater; thus, it is ideal to operate in such conditions.
Cast Iron: Cast Iron gate valves can handle water, gas, and steam.
Nickel: It is appropriate for high-pressure corrosive media applications. Nickel can function in chemical processing and nuclear power plants.
PVC: PVC can handle low temperatures and pressure media and is non-corrosive. Suitable media for this material are water, alkalis, and acids.
CPVC: CPVC has fluid requirements that are the same as PVC. One distinct difference is that it can control fluid at moderate levels.
Graphite: Ideal for handling chemicals and steam at extremely high temperatures and pressures.
Properly selecting the gate valve material enhances system performance and reduces maintenance costs. Additionally, it results in a longer lifespan for the valve. The material should also be standard and forged by trusted metal manufacturing companies.
Gate Valve Installation:
Follow these step-by-step instructions for installing gate valves.
Materials Needed:
- Gate valve.
- Pipe wrench or adjustable wrench (to tighten the valve).
- Pipe joint compound or Teflon tape (for sealing).
Steps to Install:
Gate valve installation needs careful handling of the product and tools. To begin the installation, select a specific location and shut off the water or gas supply at that point. This step is essential for safety.
Check the gate valve to ensure it fits the size of your pipe. To achieve optimal performance, ensure the valve is free of dirt or debris.

Now, put a small amount of pipe joint compound or wrap Teflon tape around the threads on both ends.
The valve should be positioned so that it turns to open or close when you want it to. Screw one end of the valve onto the pipe, turning it clockwise until it’s snug. Check if it’s straightforward with the help of a level. Gently turn the gate valve handle to test if it opens and closes smoothly. If the valve works well, you have successfully installed it correctly.
Gate Valve Maintenance Guide:
Here is the gate valve maintenance guide:
- Inspections: Gate valve inspection involves checking for signs of damage or leaks. Inspect for rust, corrosion, or loose parts over a specified period.
- Lubrication: Lubrication is essential for gate valves to smooth the movement of operating parts. Use a suitable lubricant for the stem and other moving components. Consider the manufacturer’s advice while selecting a lubricant for your product.
- Cleaning: Cleaning is one of the most accessible and primary means to maintain your gate valve. Regular cleaning of the surroundings and inner structure ensures optimal performance. It helps remove debris or other particles that could disrupt the gate valve’s operation.
- Corrosion Prevention: Gate valves exposed to harsh environments or corrosive substances may require additional protection. Consider using coatings or materials designed to resist corrosion in such situations.
- Repair Leaks: Leaks can lead to the wastage of fluids and may occur due to a faulty seal or damaged valve. Repairing leaks can make the gate valve function for a longer time.
- Keep Surrounding Area Clear: Ensure the area around the gate valve is free from obstructions, debris, or any potential hazards that could affect its operation.
- Training and Safety: Only trained personnel handle maintenance tasks for gate valves. Safety is crucial when working with valves, pipes, and pressurized systems.
Gate Valve Buying Guide:
A gate valve buying guide will help you decide when purchasing a suitable gate valve for your needs. Although gate valve price can be a significant factor, there are also a few others. Here are a few key factors to consider when purchasing a gate valve.
Valve Size:
Always opt for a gate valve that syncs with your plumbing system’s size or pipe. Gate valves are available in various sizes, so select one that matches the diameter of your pipes.
Type of Gate Valve:
Among various gate valve types, choose the one that suits your application. There are rising stem and non-rising stem gate valves and other classes with many benefits.
Pressure Rating:
The gate valve’s pressure ratings should be equal to or higher than your system pressure. It’s crucial to avoid installing a valve that cannot handle the stress, as it could lead to failure and leaks.
Temperature Rating:
Consider the temperature at which the gate valve will operate. Material selection is essential for proper media handling as per specific systems.
Flow Control:
Determine if your application requires precise flow control or only on-off operation. Gate valves are better suited for on-off control rather than regulating flow.
Conclusion:
This ultimate gate valve guide aims to teach you multiple things about the product. Gate valve working and performance are no doubt very ingenious on their own. They enable heavy-duty operations to be swift and reliable.
You should opt for a reliable brass gate valve manufacturer before selecting one. Plumberstar is a wholesale manufacturer of plumbing valves and pipe fittings. They help you get the best in the market, saving you from the fuss of unnecessary replacements and repairs.
FAQs:
Q. Can I use a gate valve for flow regulation?
Gate valves are better for on-off flow control than regulating the flow. Other valves, like globe or butterfly valves, are suitable for precise flow control.
Q. How do I maintain a gate valve?
Gate valve parts need regular maintenance. Their maintenance can be extended to inspections for damage or leaks, lubrication, and operational checks. You also need to perform cleaning, checking seals, etc.
Q. What should I do if there is a leakage in my gate valve?
Turn off the water or gas supply immediately if you notice a leak. Check for loose connections or damaged seals. If you can’t find the cause, seek assistance from a professional plumber or valve technician.
Q. Can I replace a gate valve myself?
It’s essential to have a good understanding of plumbing and gate valve installation. If you have these, you can replace a gate valve yourself.
Q. How long do gate valves last?
The lifespan of a gate valve depends on its quality, materials, usage, and maintenance. Well-maintained gate valves can last for many years if their condition is regularly monitored and they are replaced as needed.



