Hot Water Introduction
Hot water at home refers to the supply of water that has been heated. It is used for many purposes, such as bathing, washing, and cleaning. The hot water supply can come from multiple sources. These sources are a gas or electric water heater, a tankless water heater, or a heat pump water heater.
In a hot water system, cold water is supplied to a water heater, which is heated to the desired temperature. It is distributed through pipes to various fixtures in the home—the temperature of the hot water control by a thermostat on the water heater. You can control it through a thermostatic mixing valve at the point of use.
Having a reliable and efficient hot water supply is essential for modern living. It can improve comfort and hygiene. Proper maintenance and safety measures should be taken. This ensures the hot water supply is safe and free from scalding risks or Legionella bacteria growth.
What is legionella
Legionella is a type of bacteria. It can cause a severe form of pneumonia known as Legionnaires’ disease. The bacteria are found in natural water sources such as rivers, lakes, and streams. Yet, it can also grow and multiply in artificial water systems. These include cooling towers, hot tubs, plumbing systems, and decorative fountains.
Legionnaires’ disease is a severe respiratory infection. It can cause symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath, high fever, and muscle aches. The disease is not contagious. It is contracted by drinking water contaminated with Legionella bacteria.
Individuals with weakened immune systems, chronic lung diseases, or a smoking history are at a higher risk of developing Legionnaires’ disease. The condition can be ended with antibiotics and early diagnosis. Yet, the treatment is crucial for a full recovery.
What is Stagnant Water?
Stagnant water refers to any body of water that is not flowing or circulating, such as a pond, lake, or puddle. It also refers to water that is not changed. This water has been sitting in a container for an extended period.
This water is a breeding ground for;
- bacteria
- viruses
- pathogens
Mosquitoes and other insects are also attracted to stagnant water, as they use it as a breeding site. Also, stagnant water can develop an unpleasant odor and become a habitat for algae and other unwanted plant growth. It is essential to clean and maintain any bodies of water to prevent them from becoming stagnant.
How to prevent legionella?
Here are some ways to prevent legionella:
Regularly clean and disinfect water systems:
Legionella bacteria can grow in stagnant water. Yet it is vital to maintain and clean water systems regularly. This includes;
- Removing sediment and scale
- Flushing pipes and tanks
- Disinfecting the system with appropriate chemicals.
Maintain proper water temperature:
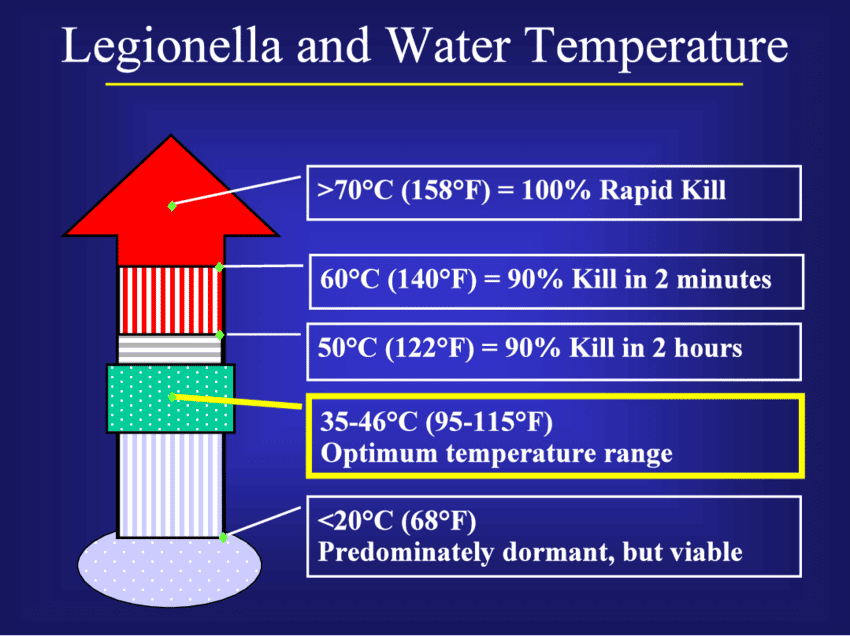
Legionella bacteria thrive in warm water. Yet, it’s essential to maintain proper temperature control. Hot water should be kept at 140°F (60°C) or higher, and cold water should be kept at 68°F (20°C) or lower.
- Avoid stagnant water:
Stagnant water is a breeding ground for this bacteria. It is crucial to avoid water systems that are not used or are left dormant for long periods.
- Use water filters:
Filters can help remove sediment and other particles from water. This can support the growth of Legionella bacteria.
- Implement a water management plan:
Hospitals, nursing homes, and hotels should have a water management plan. This system identifies and mitigates potential Legionella risks.
- Train staff and residents:
Staff and occupants should be educated about Legionella risks. Prevention measures include maintaining water systems and reporting any suspected Legionnaires disease cases.
- Seek professional help:
It is recommended to seek professional help from a qualified water treatment specialist. Consult for proper assessment, treatment, and prevention of legionella in water systems.
What is Scalding with hot water
Scalding with hot water is a burn injury that occurs when hot water comes into contact with the skin. This can cause tissue damage. Hot water scalds are a common type of scald injury ranging from mild to severe. Severity depends on the temperature of the water and the duration of contact.
Hot water scalds can occur in various settings. It includes at home, in the workplace, and in public places. Common causes of hot water scalds include
- hot showers or baths
- boiling water
- steam from a kettle or humidifier
- hot tap water.
Symptoms of a hot water scald may consist of;
- redness
- pain
- blisters
- charring or white, leathery skin.
Treatment for a hot water scald may involve first aid measures. Cool the affected area with cool running water, pain relief, and wound care. In severe cases, hospitalization and medical intervention may be necessary.
Time-Temperature Relationship in Scalds
| Temperature | Time for permanent second-degree burns | 1 minute |
| 49°C | 3 minutes | 3 minutes |
| 50°C | 1 minutes | 5 minutes |
| 52°C | 30 sec | 90 sec |
| 55°C | 5 sec | 25 sec |
| 60°C | 2 sec | 5 Sec |
| 65°C | 1 sec | 2 sec |
| 86°C | Instantaneous | 1 sec |
Prevention of scalding associated with hot water
Here are some prevention tips to avoid scalding related to hot water:
- Maintain your water heater temperature to no higher than 120°F (49°C). It will prevent hot water from reaching scalding temperatures.
- Test the water temperature before bathing, showering, or washing by turning on the cold water and adding hot water until it reaches a comfortable temperature.
- Always supervise children in the bathtub or shower and never leave them unattended.
- Use caution when filling the bathtub, as hot water can accumulate at the base and cause scalding.
- When cooking with hot water, use long-handled utensils. Try to avoid wearing loose clothing that could catch on fire.
- Use oven mitts or pot holders to handle hot dishes or appliances in the kitchen.
- Install anti-scald devices in showers, faucets, and other water outlets. These devices prevent sudden changes in water temperature.
Why do various plumbing codes and manufacturers need thermostatic mixing valves?
TMVs mix hot and cold water to maintain a consistent water temperature. TMVs are used in homes, hospitals, schools, and other facilities. It prevents scalding and provides a safe and comfortable water supply. Various plumbing codes and manufacturers need thermostatic mixing valves (TMVs). This valve ensures the safety and comfort of hot water systems. Here are some reasons why:
Legionella bacteria prevention:

The use of TMVs can also help prevent the growth of Legionella bacteria in hot water systems. These bacteria thrive in warm water, and temperatures between 95°F (35°C) and 115°F (46°C) can promote their growth. Keeping hot water temperatures above 140°F (60°C) through TMVs can reduce the risk of Legionella bacteria growth.
Scald prevention:
TMVs prevent scalding risk by mixing hot and cold water. By this, we can maintain a safe and consistent outlet temperature. Plumbing codes need TMVs to be installed in buildings. It installs in hospitals, schools, and public facilities to prevent scalding accidents.
Energy efficiency:
TMVs to control hot water temperature at the point of use. Yet, energy can be saved by reducing the need to heat water to high temperatures in a central location. This can reduce the energy consumption of the hot water system.
Ease:
TMVs can also improve the comfort of hot water systems by providing a consistent and comfortable water temperature. This can improve the user experience and prevent discomfort or complaints about inconsistent water temperature.
TMVs are essential for ensuring safety, comfort, and efficiency of hot water systems. Compliance with plumbing codes and manufacturer recommendations is vital. It prevents accidents and promotes energy efficiency. It also ensures the proper operation of the hot water system.

Where is it installed?
TMVs can be installed at the point of use, such as under a sink or shower or at the central hot water system. They can also be adjusted to provide different temperature ranges depending on the intended use, such as lower temperatures for handwashing or higher temperatures for showering or bathing.
