What is a Valve?
A valve is a fitting that regulates, controls, and directs fluids within a pipe. Turn off the water main supply in a plumbing system commonly used to control water flow. Moreover, these prevent backflow and adjust the water pressure. Homeowners can separate the sections of plumbing for repairs or close off a water line if the valves leak. They are also utilized extensively in the majority of commercial and industrial applications.
Each valve operates differently and is available in various designs to meet specific plumbing needs. Plastic, brass, bronze, lead-free brass, cast iron, and stainless steel are used to construct valves. This article will describe how some of the most common valves used in plumbing systems and their distinct applications, features, materials, advantages, and disadvantages.

Common Parts of Valves
Learn the essential components of plumbing valves by reading the list below.
Body
Cast iron, ductile iron, or steel are typically used for the primary body of an underground valve. To be durable, the primary body of the valve must be made of a material resistant to corrosion. The valve’s body is frequently coated with epoxy resin or another type of coating to reduce the danger of corrosion.
Bonnet
The bonnet of an underground valve is crucial to the valve’s overall performance. The bonnet helps seal the valve and prevents contaminants from entering the interior. The bonnet also protects the internal components of the valve from damage.
Ports
An underground valve’s ports regulate the flow of gases and liquids entering and exiting the device. Two or three ports are present depending on the size and type of the valve. Through the inlet port, fluids or gases enter the valve and exit through the outlet port. The vent port is the third port to release the valve’s internal pressure.
Actuator
A valve that is installed below ground is known as an underground valve. The actuator is the component that controls the valve’s opening and closing. Multiple actuators exist, but the hydraulic actuator is most commonly used in underground valves. Typically, hydraulic actuators are used to generate enormous pressure.
Disc
A disc is an essential component of many valves, particularly subterranean valves. Discs are constructed to withstand subterranean environments’ extreme pressures and temperatures. This is because they are manufactured from durable, sturdy materials.
Seat
The seat assists in regulating the water flow through the valve. Typically, it is made of materials that can withstand water pressure, such as metal or plastic. Typically, the seat is located near the valve’s base, where a handle or actuator can open it.
List of Valves Used in the Oil and Gas Industry
- Gate valve

The most common kind of valve in plumbing systems is the gate valve. It consists of a wedge-shaped metal gate that can be lowered (using a twist-type handle or knob) to prevent water flow or raised to begin the flow.
Because they are designed to be completely open or closed, gate valves cannot regulate water flow. If used to regulate the water flow, it can cause the valves to deteriorate. All fluids, including air, fuel gas, feedwater, steam, lubricating oil, and hydrocarbons, can be circulated through gate valves.
Gate valves are further classified into the following categories:
1. Solid wedge gate valve
2. Flexible wedge gate valve
3. OS&Y gate valve or raising stem valve
4. Non-rising stem gate valve or insider screw valve
5. Split wedge or parallel disks gate valve
Advantages of gate valves
Because the gate within the valve retracts completely into the body, the valve does not impede water passage.
Due to the slow opening and closing of the valve, the water pressure is altered progressively, thereby protecting the pipe from the water hammer noise.
Technical Data for Gate Valve
| Size | Pressure |
| 1/2″ (DN 15) | 16bar/232psi |
| 3/4″ (DN 20) | 16bar/232psi |
| 1″ (DN 25) | 16bar/232psi |
| 1″1/4 (DN 32) | 16bar/232psi |
| 1″1/2 (DN 40) | 16bar/232psi |
| 2″ (DN 50) | 16bar/232psi |
| 2″1/2 (DN 65) | 16bar/232psi |
| 3″ (DN 80) | 16bar/232psi |
Quick Tip:
Gate valves are designed for entirely opened/closed applications. They should not be used for “throttling” or adjusting the flow, as water movement against only a portion of the gate could cause damage. Remember that gate valves can seize or become obstructed after extended periods of only being opened or closed.
- Globe valve
Globe valves are used to open, close, and control fluid passage. Like ball and gate valves, globe valves are designed to modulate and restrict water flow. The body’s globe-shaped valve (hence the name “globe”) contains a stationary ring seat. When the handwheel knob is turned, a disc-shaped device is released from the ring seat and spins upward. It allows water to pass through a Z-shaped passage from one chamber to another. The lever can be fully opened, completely closed, or partially opened to control the water flow and water pressure. They function similarly to a kitchen faucet or outdoor irrigation hose bib in this capacity.
As with a ball or gate valve, globe valves can be isolated. Globe valves, however, exhibit a greater pressure decrease than conventional shut-off valves. The curved Z-shaped interior of the valve restricts the passage of fluids or steams more than the gate and ball valves, so they are ideal for use at lower pressures. However, because globe valves close and open slowly, they can be used to prevent water impact. They are also not susceptible to leaking at moderate pressure.
Globe Valve Applications:
• It is utilized in high-point vents and low-point drainage when leak tightness and safety are paramount. Otherwise, you can drain and exhaust using a gate valve.
• It can be used in feed water, chemical, air, lubricating oil, and almost all other services where pressure decrease is not an issue.
• This valve is also utilized as an automatic control valve. Still, the valve’s stem is smooth rather than threaded in that case. Yet it is opened and closed by lifting the action of the actuator assembly.
- Butterfly valve

A butterfly valve is another type of shut-off valve that can also be used to control water flow. A butterfly valve’s disc opens and closes the valve. A quarter turn of the handle adjusts the position of this moving part, much like a ball valve. This disc opens up as the handle is cranked. It allows water to flow through the faucet. The closure of the disc prevents the passage of fluids. Butterfly valves are the smallest in the family of “rotary motion” valves, including ball and plug valves. This is because they utilize a revolving mechanism to close the flow when in control.
A pressure decrease occurs whenever a butterfly valve is opened. When turned on, the disc rotates, directing water to flow around it. The pipeline is always impaired while a butterfly valve is open, limiting its use. However, the disc’s ability to rotate on an axis makes these valves simpler to operate by hand in the face of incoming water pressure.
The butterfly valve’s benefits:
• Convenience: butterfly valves require far less room than other valves, particularly industrial ones. They are small and simple to set up and run without any hiccups. They are widely used in the business world due to
simple installation.
Butterfly valves tend to be inexpensive compared to other valves (such as gate valves). Due to their low material and labor costs, butterfly valves are among the most economically advantageous.
Types of Butterfly Valves
- Double offset butterfly valve
- Triple offset butterfly valve
- Flanged ends
- Wafer type ends
- Lug type ends
- Butt-welded types end
- Zero offset butterfly valve
- Stop Valve (Straight & Angled)

Although any valve can work as a stop (blocking flow from the main supply), some valves are specifically designed for this function. You’ll find them behind your toilet, under your sink, and in other supply fixtures. They provide a shut-off mechanism for these supplies, frequently extending from a wall and moving up or down to reach them. When everything falls into place, a straight stop valve is required. These valves may utilize three primary internal mechanisms: ball, globe, or gate. Their designs result in less flow restriction than the alternative (using a standard globe valve and elbow), so they are preferred over the alternative.
The majority of angle or straight stops are compressions or 1/4-turn designs. A 1/4-turn valve is a valve that is activated by a quarter-turn of the handle, as opposed to one or more complete rotations as with a compression valve. These valves, typically ball valves, are not intended for throttling but for fast, convenient shut-off of fixtures such as toilets and sinks.
- Check valves

Your plumbing should only allow water to flow in one direction, either from the supply pipes to the fixture, out or from the fixture to the drain, and then into the sewage main. A check valve (backflow prevention) is required to ensure a one-way flow in the event of a “cross-connection” (wastewater flowing reverse into the supply). When the flow is reversed, a ball is sometimes used to plug the hole. A flapper is used to do a swing check valve, which is positioned by water flowing in the opposite direction. Some devices use discs mounted on springs or diaphragms. These check valves are known as “non-operational” because they do not rely on human intervention. Instead, they rely on the laws of physics to operate independently. Look for a stop-check if you need a functional check valve; these still function automatically but can be shut off manually for one or both flow directions. A reduced pressure zone assembly (RPZA) is one example of a device that combines a check valve with additional components to prevent backflow.
Application
Safety applications, pumps, sprinkler systems, and any other home plumbing vulnerable to continual or intermittent backflow can all benefit from installing check valves.
Key point:
Check valves with a spring mechanism that permits them to close before the backflow hits are available. These can significantly lessen the possibility of water hammer.
6. Ball Valve

Ball valves are the most trusted and widely used water flow control valves. The valve is turned by rotating a sphere containing a hole connected to a lever.
When the sphere is open, the hole is aligned with the pipe, and water can flow freely. The water flow is entirely blocked when the sphere is closed because the hole is perpendicular to the pipe. The valve’s open/closed status can be seen by looking at the lever handle. A closed valve is achieved by positioning the lever perpendicular to the pipe.
Ball Valves: Types
- 3 Way ball valve
- Three-piece body
- Trunnion-mounted ball valve
- Floating ball valve
- Side entry or split body
Advantages
- One major benefit of ball valves is that they provide an excellent seal in the closed position.
- It is smaller and lighter than a gate valve of the same rating and size.
Ball Valve Technical Data
| Size | D | L | H |
| ¼ inch | 0.23 | 2.99 | 2.20 |
| 3/8 inch | 0.32 | 2.99 | 2.20 |
| ½ inch | 0.51 | 4.02 | 2.20 |
| ¾ inch | 0.75 | 4.25 | 2.72 |
| 1 inch | 0.99 | 4.53 | 3.50 |
| 1 ½ inch | 1.50 | 5.24 | 4.49 |
| 2 inch | 1.89 | 6.06 | 4.72 |
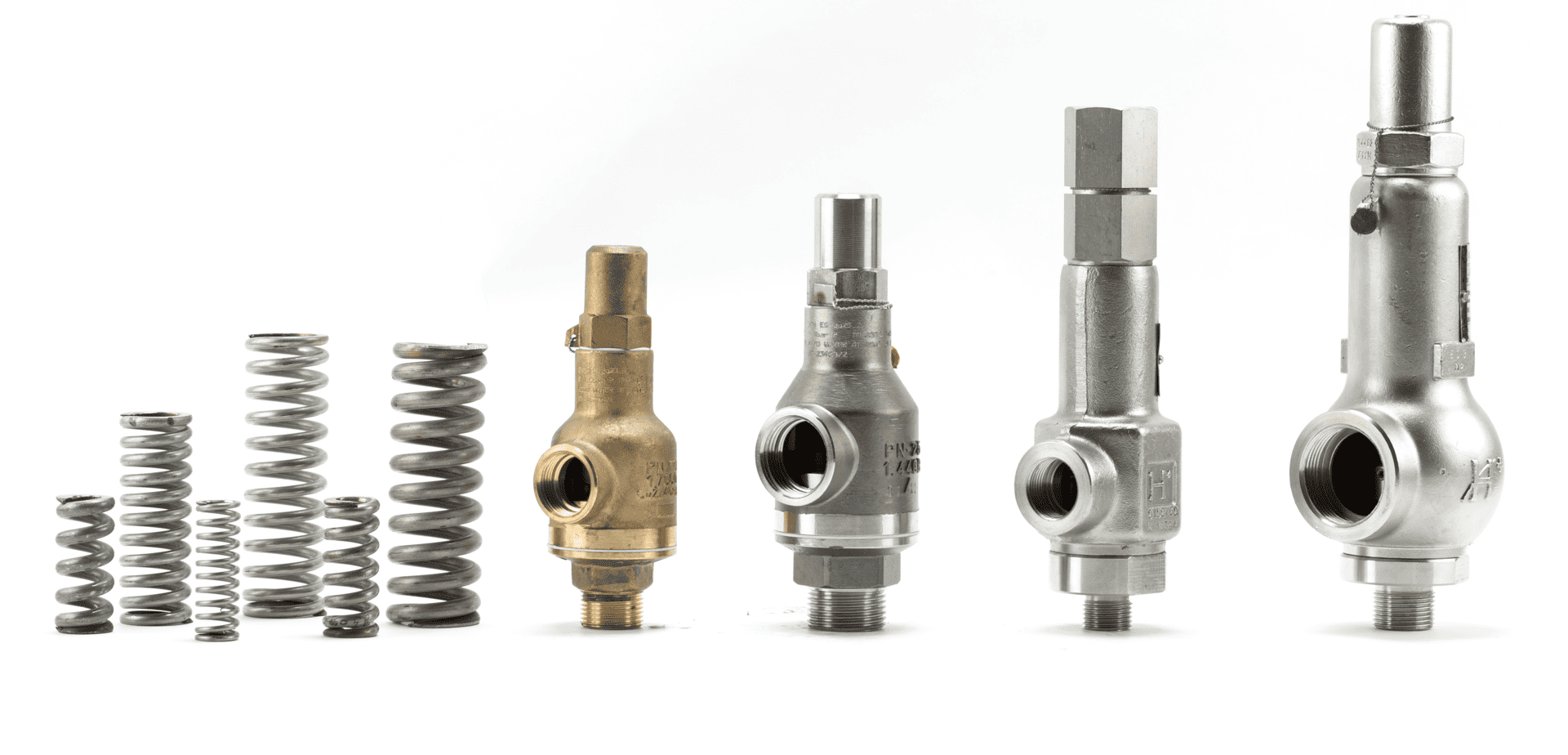
7. Pressure Relief Valves
Common names for pressure relief valves include pressure-reducing valves and pressure balance valves. They prevent pipes from bursting by doing what their names imply (relieving, balancing, or reducing pressure in pipes). In addition, the water pressure can be limited to whatever level is appropriate for your plumbing and pipes.
Pressure relief valves use an internal spring and diaphragm to regulate the water pressure to set maximum and minimum values. The disc within is held in place by a disk holder shaped like a ring.
The water pressure entering the ring seat is controlled by the spring’s pressure on the disk holder and its disk. These valves have many uses and can be found in various places, including fire hoses, water tanks, water towers, and high-rise buildings.
Advantages of Pressure Relief Valves
- It is versatile and used in various services like water tanks, drinking water applications, water, towers, high rise, and firefighting.
- Extremely reliable if sized and used appropriately
8. Plug valve
A plug valve is a circular flow-isolating or flow-directing valve. Within the plug, the valve is cone-shaped. Like a ball valve, the plug valve has a hole through its center. When the handle is turned a quarter turn, the cork rotates to face the approaching water flow and opens the passage. When the valve is closed, the porous center aligns with the valve walls, stopping the flow. Multiple-port plug valves could also be used to divert flow across multiple channels.
Plug valves are constructed relatively simply and can be opened with a quarter-turn lever. Plug valves function similarly to ball valves because their design predates the ball valve. Although plug valves are no longer as prevalent as ball valves, they are a suitable alternative. These valves are manufactured with either lubricating or non-lubricating designs and a variety of port ports opening via plugs.
Plug valves can be constructed with “full ports,” allowing full fluid passage through the valve, or with narrower cores. This will create resistance to flow and allow the flow to be regulated. Plug valve ports are typically diamond-shaped, rectangular, or circular. Circular and rectangular openings permit unrestricted flow, whereas diamond ports restrict flow. In contrast, plug valves should not be used to control flow.
- Expanding plug
- Eccentric plug
- Lubricated plug
- Non-lubricated
Things to Consider When Purchasing the Valve
With so many options, it’s important to consider all aspects to ensure you choose the right water valve for your needs. Here are some points to start:
• How valves work:
Find out how big a gap your valve needs to fill. 2-way valves are best for on and off in a system, while 3-way valves can control on and off and mix fluids. Keep in mind whether your valve will be mostly closed or mostly open. Order a valve that normally opens this way but the other way when it gets power. This will make it last longer.
• Requirements for Upkeep:
If frequent maintenance is needed, ball valves are a good choice because they don’t get clogged and are one of the easiest valve types to fix. Ball valves can also be bought in three-piece sets with two end closures and a body. The main body is straightforward to clean without taking the end caps off the pipe. This keeps the line from shutting down while maintenance is required.
• Type of Media:
The material of the valve will depend on the qualities of the gas or liquid being controlled. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and perfluoroalkoxy alkanes (PFA) are great alternatives for monitoring harsh or corrosive compounds. They can withstand these circumstances. Metallic valves should be used to control high-pressure gases for the best level of safety.
Important Material for Valve Manufacturing
A valve in plumbing is a mechanical device that controls how fluids move. There are many different kinds of valves, and each one is used for different purposes. But there is one thing that all valves have in common: they are all made of almost the same materials.
The metal is considered one of the most important materials for valve manufacturing. What kind of metal is used will depend on the valve used. For example, brass is often used to make valves that control water flow because it doesn’t rust.
Stainless steel is also often used for valves because it can handle changes in temperature and pressure well. These are also made of PVC, bronze, and other materials.
In addition to the metal used to make the valve’s body, it also needs other materials to work right. The valve’s seats and seals must be made of materials that work well with the maintained fluid. Rubber or plastic are two materials that are often used for this. Lubricants may be needed to keep the valve’s moving parts working smoothly.
