Introduction of pressure regulating valve
A pressure-regulating valve is a device that regulates fluid pressure in a system. It maintains the pressure within a specific range. It also prevents damage to the system and ensures optimal performance. The valve consists of components that work together to keep the pressure standard.

| Specifications. Product: Water Pressure Regulator Valve. Material: Bronze Raw Material. Size: 1/2″-2″ Working Pressure: 25 Bar. Thread Type: NPT. Applications: Water-Related Applications. |
Types of Pressure Regulating Valves:
There are several pressure-regulating valves, each with its own design and functionality. Here, we will discuss the three most common types of pressure-regulating valves.
Direct-Acting Pressure Regulating Valve:
Direct-acting pressure-regulating valves are the primary type of pressure-regulating valve. They consist of a diaphragm, a spring, and a valve seat. When the pressure on the downside of the valve is below the setpoint, the diaphragm moves upward. It opens the valve and allows fluid to flow through it. When this pressure exceeds the setpoint, the diaphragm moves downward. It closes the valve and reduces the flow of fluid.
The diaphragm is made of rubber or other flexible material. It handles keeping the pressure changes into a mechanical motion. The spring provides a constant force against the diaphragm. It opposes the upstream pressure and helps to maintain consistent pressure.
Direct-acting pressure-regulating valves are simple and reliable. Yet, they have limitations in regulating high flow rates. We use them in small-scale HVAC, water heaters, and irrigation systems.
Pilot-Operated Pressure Regulating Valve:
Pilot-operated pressure-regulating valves are more complex than direct-acting valves. They are capable of regulating much higher flow rates and pressure differences. They consist of a pilot valve and a central valve. They both work together to control the pressure.

The pilot valve senses the downstream pressure and opens or closes the main valve. When the downstream pressure drops below the setpoint, the pilot valve opens. It allows the upstream pressure to move the main valve and increase the fluid flow. When the downstream pressure exceeds the setpoint, the pilot valve closes. It reduces the flow of fluid.

We use them in oil and gas pipelines, steam systems, and chemical plants. They can handle high flow rates and pressure drops. These are often used when we want precise control over the pressure.
Relief Valve:
Relief valves are a type of pressure-regulating valve. The design of these valves protects equipment and systems from overpressure. We use them in systems that have the potential to experience pressure spikes or surges. Their applications are hydraulic systems, boilers, and gas pipelines.
Relief valves open when the pressure in the system exceeds a setpoint. When the valve opens, it allows fluid to escape from the system. It reduces the stress until it returns to a safe level. The valve then closes and remains closed until the pressure gets normal.
Relief valves are critical safety devices. They can prevent catastrophic failures and protect personnel from injury or death. They must have an appropriate size.
Working Mechanism of Pressure Regulating Valves:
Pressure-regulating valves work on a standard principle. They balance the pressure on the valve’s inlet against a set pressure on the outlet. The process involves using a spring or other mechanical device that provides a force. This force opposes the pressure on the inlet side of the valve.
When the pressure on the inlet side of the valve exceeds the set pressure on the outlet side, the valve will open. It lets some of the fluid flow through the valve. It also reduces the stress on the inlet side. The valve will close when the pressure on the inlet side is lower than the set pressure on the outlet side. It prevents extra fluids from flowing through the valve. It also increases the pressure on the inlet side.
The mechanism for regulating pressure can vary depending on the type of valve we use. For example, direct-acting valves have flexible diaphragms and springs to handle fluids. The diaphragm attaches to a valve stem. It controls the flow of liquid or gas through the valve. As the pressure on the inlet side of the valve increases, it exerts a force on the diaphragm. It compresses the spring and moves the valve stem to open the valve.
Pilot-operated valves use a similar principle. They have two valves working together to control fluid or gas flow. The pilot valve senses the pressure on the outlet side of the main valve and opens or closes the main valve. Relief valves operate in a different manner from direct-acting and pilot-operated valves. Relief valves’ design release excess pressure when it exceeds a certain setpoint.
When the pressure in the system exceeds the setpoint, the relief valve opens. It allows fluid or gas to escape and reduce stress. Once the pressure has returned to a safe level, the valve closes.
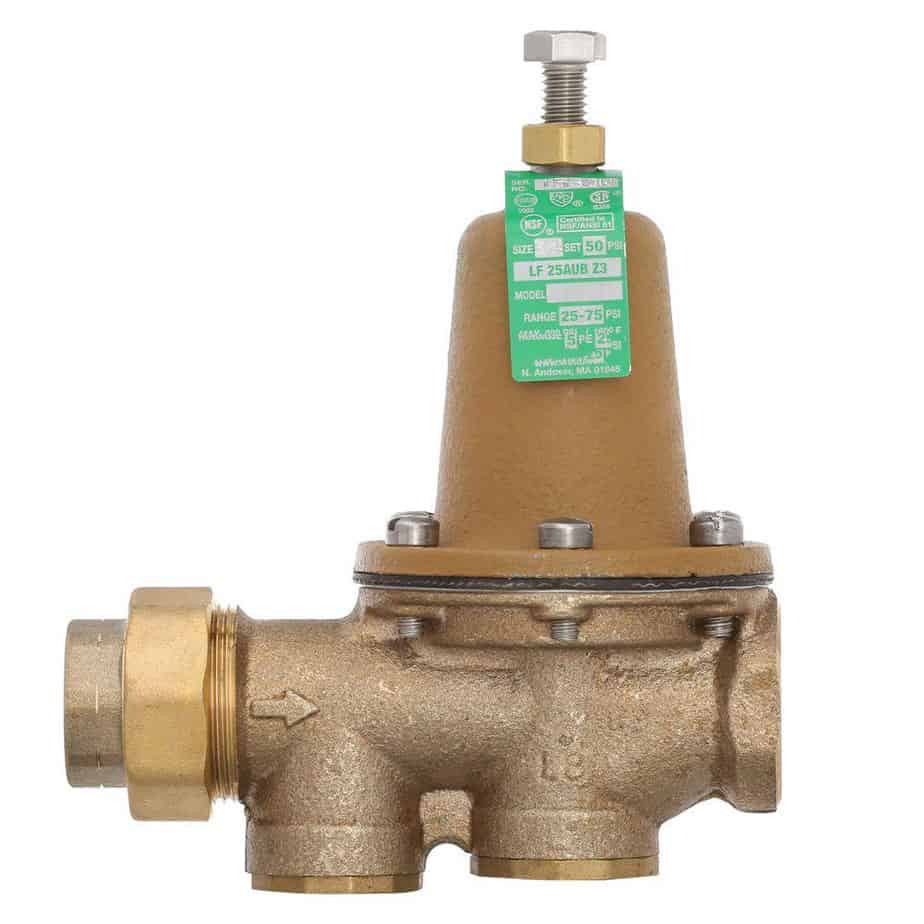
Parts of Pressure Regulating Valves:
A pressure-regulating valve has several parts that work together to regulate the pressure. The main components of a pressure-regulating valve include:
Body: The body holds all the other components. It consists of materials like brass, stainless steel, or plastic. The material of the body depends on the application and the fluid we are regulating.
Inlet port: The inlet port is the entry point for the fluid into the valve. It is present on the side of the valve body. The inlet may include a filter or strainer to remove debris from the liquids.
Outlet port: The outlet port is the exit point for the fluids from the valve. It lies on the opposite side of the valve body from the inlet port.
Valve stem: The valve stem is a long, narrow rod connecting the valve body to the disc. When we actuate the valve, the valve stem moves the disc up or down. It adjusts the flow through the valve.
Valve disc: The valve disc is a circular plate inside the body. It controls the flow of fluid or gas. It connects to the valve stem and moves up or down depending on the pressure in the system.
Spring: The spring maintains the desired pressure range. It lies inside the valve body and attaches to the valve disc or stems. The spring applies a force to the valve disc. It keeps the valve closed until the pressure in the system exceeds the desired range.
Diaphragm: Some pressure-regulating valves feature a diaphragm. It is a flexible membrane separating the spring from the fluid we regulate. The diaphragm helps to isolate the spring from the process liquids. It is often necessary for some systems.
Adjusting screw: The adjusting screw is a small screw on the top of the valve body. It allows the user to adjust the pressure range of the valve. By turning the adjusting screw, the user can increase or decrease the force applied by the spring. The process, in turn, affects the pressure range of the valve.
Maintenance of Pressure Regulating Valves:
Maintaining pressure-regulating valves is essential to ensure proper operation and prevent potential damage. Here are some important maintenance tasks to perform on pressure-regulating valves:
- Regular inspection of valves can help identify any signs of damage. Inspect the valves for any visual signs of corrosion or rust on the valve body or other components.
- Clean valves: Regular cleaning of valves prevents blockage and ensures proper function. We can clean the valves by wiping them down with a damp cloth. We can also use a cleaning solution suitable for the valve material.
- Lubricate valves: Regular lubrication of valves can prevent them from becoming stiff. Apply a small amount of lubricant to the valve stem and other moving parts. Make sure to follow the instructions from the maker.
- Check valve seating: The valve seating is where the valve closes against the valve body. Ensure that the seating is not damaged or worn out because it can lead to leakage. Check the seating by removing the valve and inspecting the surface for damage.
- Replace Damaged Parts: If the valve parts are damaged, you should replace them. Damaged pieces can affect the valve’s ability to regulate pressure. It can be problematic if you ignore it.
- Test the valve: Regular valve testing is necessary to ensure proper operation. Test the valve by increasing and decreasing the pressure on the inlet side of the valve. You can verify that the valve opens and closes as expected. If the valve fails the test, we should repair it or replace it.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations. The package has instructions for the maintenance and operation of the valve. It includes intervals for inspection, cleaning, and replacement of parts.
Make sure that only qualified personnel should maintain the pressure-regulating valves. The person should be trained to work with valves and have the appropriate tools. Improper maintenance can lead to valve malfunction, resulting in System failure. Maintaining pressure-regulating valves is essential to ensure their proper function. Prevent potential damage to equipment or systems. Regular inspection, cleaning, and testing can add to a Valve’s lifetime. These are essential maintenance tasks to perform on pressure-regulating valves. We can enhance the performance of the valve through maintenance. It results in efficient and reliable pressure control for various applications.
Applications of Pressure Regulating Valves:
Pressure-regulating valves have a wide range of applications in industries. Here are some of the most common applications of pressure-regulating valves:
Water Supply Systems: We use Pressure-regulating valves in water supply systems. They maintain consistent water pressure. It is vital in tall buildings where the water pressure can fluctuate. Pressure-regulating valves help to ensure that water flows evenly throughout the system. It prevents damage to pipes and fixtures.
Gas Transmission and Distribution: We use them in gas transmission and distribution systems. Pressure Pressure-regulating valves maintain safe gas pressure. Such systems operate under high pressure. Regulating valves is critical for ensuring the pressure remains within a safe range. They are also used in gas-fired equipment such as boilers and ovens.
Oil and Gas Industry: Pressure-regulating valves have vast use in the oil and gas industry. They regulate the pressure of fluids and gases in pipelines and plants. They are also used in drilling operations to control the pressure of drilling fluids.
Pharmaceuticals: Pressure-regulating valves are applicable in pharmaceuticals to regulate pressure. We use them in chromatography, fermentation, and filtration. They are also used to produce medical gases such as oxygen and nitrogen.
Food and Beverage Industry: We use these valves in the food and beverage industry. They are applicable in distilling, brewing, and carbonation. They are also used to produce compressed air for packaging and bottling operations.
HVAC Systems: We use Pressure-regulating valves in (HVAC) systems to regulate air pressure. They help to ensure that the airflow is consistent throughout the system. They prevent damage to equipment and ensure optimal performance.
Aerospace Industry: We use Pressure-regulating valves in fuel, hydraulic, and pneumatic systems. They also produce compressed air for plane engines and other methods.
Industrial Manufacturing: Pressure-regulating valves have various industrial manufacturing applications to regulate pressure. We use them in processes such as welding, cutting, and brazing. They are also used in compressed air systems for powering tools and equipment.

Conclusion:
Pressure-regulating valves offer several advantages in various applications. It includes accurate pressure control, safety, and flexibility. Pressure Pressure-regulating valves are a great solution to pressure problems. They are cost-effective and easy to operate. Industries have extensive use of these valves. They are also applicable to household uses.
A Pressure-regulating valve increases the efficiency of the system. It saves the equipment from overpressure. The structure of these valves is quite relatable. Installing pressure Regulating valve improves the performance of the system. Yet, the selection of a suitable type is vital. Buyer should consider the desiring details for the application of the valve. It increases the compatibility of the product and the equipment.
